Shipping calculated at checkout
Couldn't load pickup availability
Questions about this product? Ask our scientist!
Minute™ Single Cell Isolation Kit for Fresh and Fixed Tissues (50 Preps)
SKU:Cat #: SC-012
Manual & Protocol | MSDS
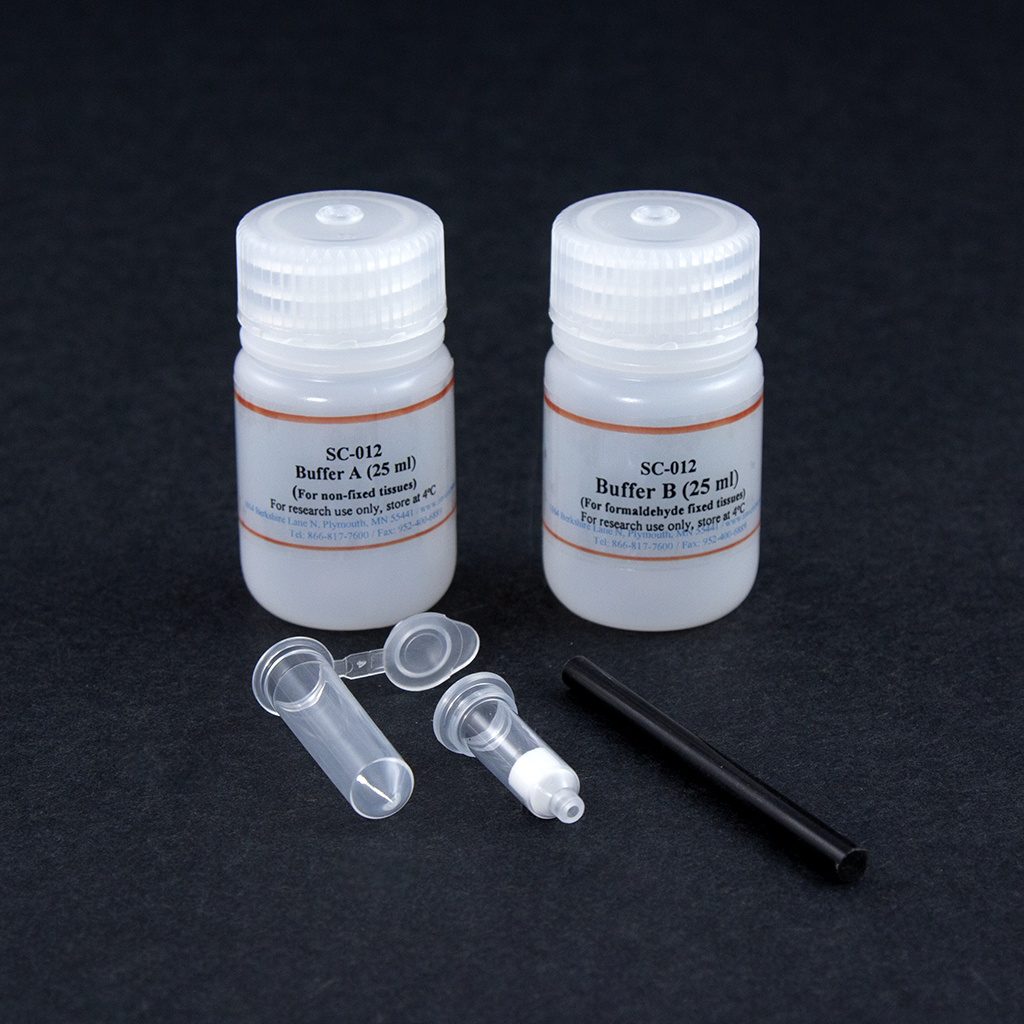
MinuteTM single cell isolation kit comprises optimized tissue disaggregation buffers and specially designed filter cartridges with 2.0 ml collection tubes. The kit is designed to isolate single cells from fresh animal tissues rapidly, and it can also isolate nuclei from tissues briefly fixed with formaldehyde for chromosome immunoprecipitation (ChIP). The tissue disaggregation buffers are formulated to disaggregate animal tissues gently. The buffers don’t contain any proteinases and EDTA that may adversely affect cell surface markers. Due to filter cartridges with pre-defined pore size and a specially formulated buffer system, single-cell suspension can be obtained from fresh tissues in less than 10 min. This kit is specifically designed for lymphoid tissues such as the spleen, thymus, and lymph node. For other tissues, the performance is tissue type-dependent. For cell suspension isolation from frozen/fresh tissues, please refer to Cat# CS-031.


Kit includes:
|
Items
|
Quantity |
|
Buffer A (for non-fixed tissues) |
25 ml |
|
Buffer B (for fixed tissues) |
25 ml |
|
Cell Isolation Filter Cartridges |
50 units |
|
Collection Tubes with Caps |
50 units |
|
Plastic Rods |
2 units |
References (8)
- Kuo C-T, et al. (2016). Optical painting and fluorescence activated sorting of single adherent cells labelled with photoswitchable Pdots. Nature Communications. http://www.nature.com/naturecommunications.
- Bultmann-Mellin, I., Dinger, K., Debuschewitz, C., Loewe, K. M., Melcher, Y., Plum, M. T., ... & Jüngst, C. (2017). Role of LTBP-4 in alveolarization, angiogenesis and fibrosis in lungs. American Journal of Physiology-Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology, ajplung-00031.
- Vergara, M. N., Flores-Bellver, M., Aparicio-Domingo, S., McNally, M., Wahlin, K. J., Saxena, M. T., ... & Canto-Soler, M. V. (2017). Enabling quantitative screening in retinal organoids: 3D automated reporter quantification technology (3D-ARQ). Development, dev-146290.
- Janicova, A., Becker, N., Xu, B., Wutzler, S., Vollrath, T., Hildebrand, F., ... & Relja, B. (2019). Endogenous uteroglobin as intrinsic anti-inflammatory signal modulates monocyte and macrophage subsets distribution upon sepsis induced lung injury. Frontiers in Immunology, 10, 2276.
- Tanaka, M., Saka-Tanaka, M., Ochi, K., Fujieda, K., Sugiura, Y., Miyamoto, T., ... & Aoe, S. (2020). C-type lectin Mincle mediates cell death–triggered inflammation in acute kidney injury. Journal of Experimental Medicine, 217(11).
- Becker, N., Störmann, P., Janicova, A., Köhler, K., Horst, K., Dunay, I. R., ... & Relja, B. (2021). Club Cell Protein 16 Attenuates CD16brightCD62dim Immunosuppressive Neutrophils in Damaged Tissue upon Posttraumatic Sepsis-Induced Lung Injury. Journal of Immunology Research, 2021.
- Günther, H. S., Henne, S., Oehlmann, J., Urban, J., Pleizier, D., Renevier, N., ... & Wülfing, C. (2021). GFAP and desmin expression in lymphatic tissues leads to difficulties in distinguishing between glial and stromal cells. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1-14.
- Kawada, M., Yokoi, H., Kimura, T., Matsumoto, Y., Sakurai, H., Matsumoto, K., ... & Saito, K. (2021). Involvement of galanin and galanin receptor 2 in a mouse model of allergic rhinitis. Allergology International.