Shipping calculated at checkout
Couldn't load pickup availability
Questions about this product? Ask our scientist!
Minute™ High-Efficiency Exosome Precipitation Reagent (20 ml)
SKU:Cat #: EI-027
Manual & Protocol | MSDS
Exosomes are vesicles secreted by cells. They are present in a variety of body fluids such as serum, ascites, spinal cord fluid, urine, and saliva. Cultured cells also secrete significant number of exosomes. The size distribution of exosome is ranging from 30-120 nm. The biological function of exosomes is believed to serve as intercellular messengers. Filtration and ultracentrifugation are classical ways of isolating and enriching exosomes. This is a tedious process and requires special equipment. Another common way for enrichment of exosome is through precipitation. Currently major commercial kits are PEG-based. EI-027 is designed to precipitate total exosomes from biofluids using a high efficacy, non-PEG based reagent for exosome precipitation. This kit is suitable for routine biofluid samples using the same reagent and similar protocol.
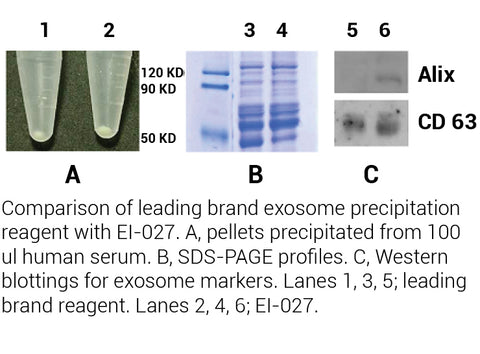
Kit includes:
|
Item |
Quantity |
|
Exosome Precipitation Reagent |
20 ml |
References (11)
- Bai, H., Pan, Y., Qi, L., Liu, L., Zhao, X., Dong, H., ... & Wang, X. (2018). Development a hydrazide-functionalized thermosensitive polymer based homogeneous system for highly efficient N-glycoprotein/glycopeptide enrichment from human plasma exosome. Talanta.
-
Jiao, F., Xia, C., Zhao, Y., Ying, W., Xie, Y., Guan, X., ... & Qian, X. (2018). A novel strategy for facile serum exosome isolation based on specific interactions between phospholipid bilayers and TiO2. Chemical Science.
- Tan, Y., Nie, W., Chen, C., He, X., Xu, Y., Ma, X., ... & Wang, W. (2019). Mesenchymal stem cells alleviate hypoxia-induced oxidative stress and enhance the pro-survival pathways in porcine islets. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 1535370219844472.
- Cheng, P., Feng, F., Yang, H., Jin, S., Lai, C., Wang, Y., & Bi, J. (2020). Detection and significance of exosomal mRNA expression profiles in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with meningeal carcinomatosis. Journal of Molecular Neuroscience, 1-14.
- Lu, T., Zhang, Z., Zhang, J., Pan, X., Zhu, X., Wang, X., ... & Yan, M. (2022). CD73 in small extracellular vesicles derived from HNSCC defines tumour‐associated immunosuppression mediated by macrophages in the microenvironment. Journal of Extracellular Vesicles, 11(5), e12218.
- Theel, E. K., & Schwaminger, S. P. (2022). Microfluidic Approaches for Affinity-Based Exosome Separation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(16), 9004.
- Omrani, M., Beyrampour-Basmenj, H., Jahanban-Esfahlan, R., Talebi, M., Raeisi, M., Serej, Z. A., ... & Ebrahimi-Kalan, A. (2023). Global trend in exosome isolation and application: an update concept in management of diseases. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 1-13.
- Omrani, M., Beyrampour-Basmenj, H., Jahanban-Esfahlan, R., Talebi, M., Raeisi, M., Serej, Z. A., ... & Ebrahimi-Kalan, A. (2023). Global trend in exosome isolation and application: an update concept in management of diseases. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry, 1-13.
- Cheng, C., Wang, P., Yang, Y., Du, X., Xia, H., Liu, J., ... & Liu, Q. (2023). Smoking‐Induced M2‐TAMs, via circEML4 in EVs, Promote the Progression of NSCLC through ALKBH5‐Regulated m6A Modification of SOCS2 in NSCLC Cells. Advanced Science, 2300953.
-
Chen, G., Pu, G., Wang, L., Li, Y., Liu, T., Li, H., ... & Luo, X. (2023). Cysticercus pisiformis-derived novel-miR1 targets TLR2 to inhibit the immune response in rabbits. Frontiers in Immunology, 14.
- Cheng, C., Wang, P., Yang, Y., Du, X., Xia, H., Liu, J., ... & Liu, Q. (2023). Smoking‐Induced M2‐TAMs, via circEML4 in EVs, Promote the Progression of NSCLC through ALKBH5‐Regulated m6A Modification of SOCS2 in NSCLC Cells. Advanced Science, 2300953.

