Shipping calculated at checkout
Couldn't load pickup availability
Questions about this product? Ask our scientist!
Minute™ Single Nucleus Isolation Kit for Neuronal Tissues/Cells (20 preps)
SKU:Cat #: BN-020
Manual & Protocol | MSDS
*Invent Biotechnologies, Inc. is the inventor of the spin column-based cell fractionation technology (including single nuclei isolation). We have not authorized third parties to produce similar products using the technology.
Isolated nuclei are widely used for various experiments such as FACS, single nucleus analysis (such as RNA-seq and ATAC-seq), immunofluorescence staining, cell cycle, and apoptosis research. Single-cell RNA-seq is a powerful technology for studying the complex cellular composition of tissues. However, Neurons are highly interconnected, and it is challenging to obtain single cells from neuronal tissues such as the brain and spinal cord. It is even more difficult to isolate intact cells from frozen neuronal tissues. Due to these limitations, single-cell RNA-seq is being substituted by single-nucleus-seq. The traditional method for single nucleus isolation from neuronal tissue is relatively tedious and time-consuming, and the yield is usually low because it is difficult to get rid of contaminating myelin and other cellular components. This kit is designed to address the issues with a simple, rapid, and effective protocol. The highly purified single nucleus can be obtained in about 30 min. Compared to the traditional method, the kit requires much less starting material and can handle an extensive range of sample sizes (1-25 mg). The buffers contain a proprietary mix of detergents for efficient cell lysis. If the presence of detergent is not desirable, a detergent-free nuclei isolation kit is also available under cat# NI-024.
For storage and transportation of isolated single nuclei, the following buffer is recommended:
WA-014: Minute™ Anti-Clumping Nuclei Storage Buffer
NOTE: We also offer the following single nucleus isolation kits depending on the tissue types and resistance to exposure of detergent:
NI-024: Minute™ Detergent-Free Single Nuclei Isolation Kit
SN-047: Minute™ Single Nucleus Isolation Kit for Tissues/Cells
AN-029: Minute™ Nuclei and Cytosol Isolation Kit for Adipose Tissues/Cultured Adipocytes

Nuclei Isolated from zebrafish brain tissue Using BN-020 and stained with DAPI (False-coloured in green) (Courtesy Sema Elif Eski, Singh Lab, Université Libre de Bruxelles).




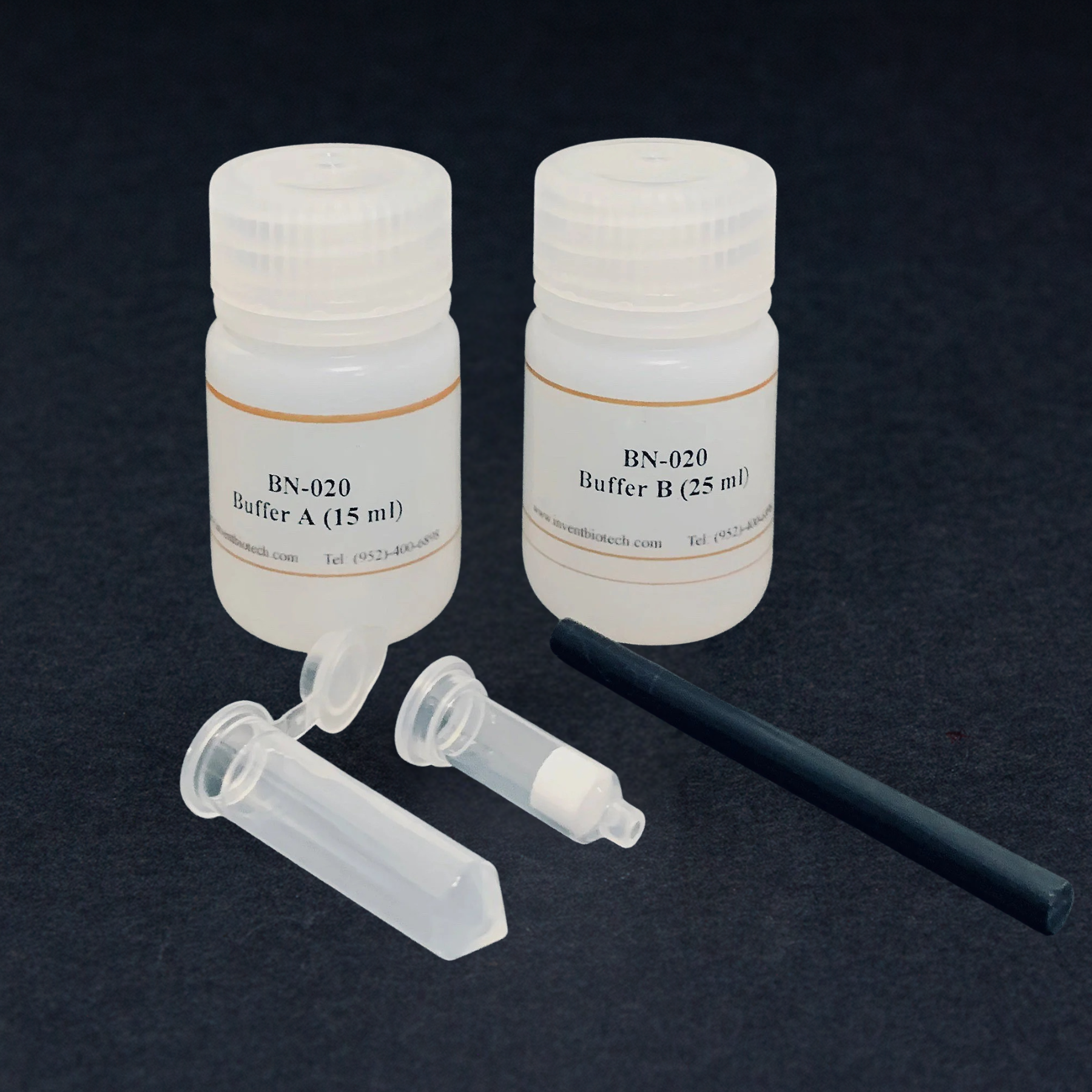
Kit includes:
|
Items |
Quantity |
|
Buffer A |
15 ml |
|
Buffer B |
25 ml |
|
Pestles for 1.5 ml Tubes |
2 units |
|
Filter Cartridge with Collection Tubes |
20 units |
References